What are the key differences in battery technology used in 4-wheel mobility scooters?
The key differences in battery technology used in 4-wheel mobility scooters include:
Battery Type:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
Pros: Generally more affordable and widely available. Proven technology with reliable performance.
Cons: Heavier, bulkier, and have a shorter lifespan compared to newer technologies. They also require more frequent maintenance and have longer charging times.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Pros: Lighter, more compact, and have a longer lifespan. They charge faster and are more energy-dense, offering greater range on a single charge. They also require less maintenance and have better performance in extreme temperatures.
Cons: Higher initial cost, though prices are decreasing as technology advances.
Capacity and Range:
Amp-Hour (Ah) Rating:
Higher Ah ratings generally mean a larger battery capacity, which can result in a longer range before needing a recharge. Mobility scooters with larger batteries can travel further distances on a single charge.
Voltage:
Most mobility scooters use 12V batteries, but some high-performance models may use 24V or 36V systems. Higher voltage systems can provide more power, potentially offering better performance and longer range.
Charging Time:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
Typically have longer charging times, often requiring 8-12 hours for a full charge.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Generally charge much faster, often taking 4-6 hours or less to reach a full charge, which enhances convenience for users.
Maintenance Requirements:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
Require periodic maintenance, including checking water levels and ensuring proper ventilation to avoid off-gassing.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Require minimal maintenance and are typically maintenance-free. They do not suffer from the same issues of gassing or water loss.
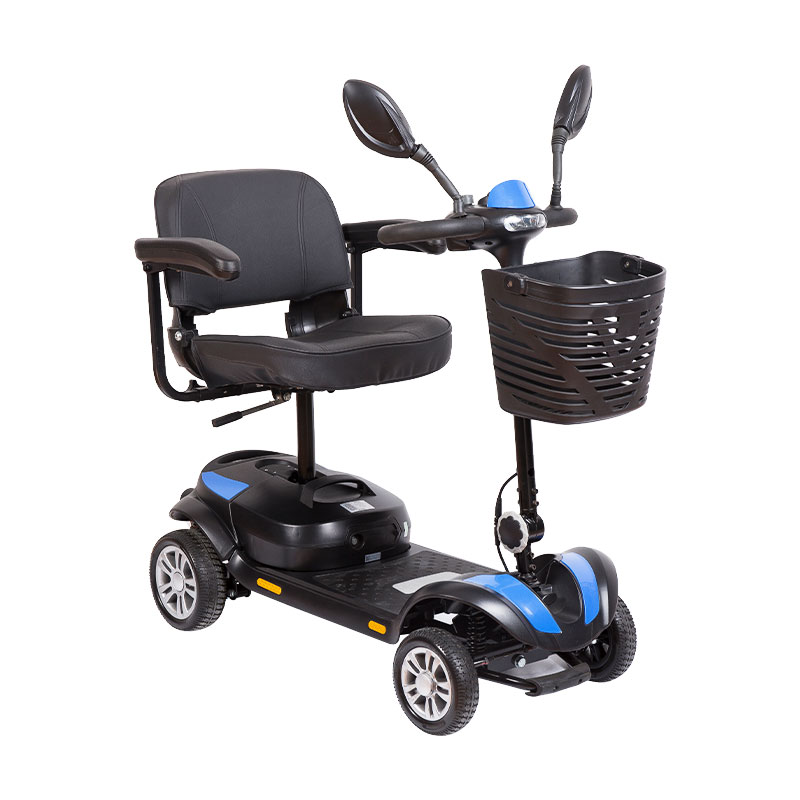

Weight and Size:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
Heavier and bulkier, which can impact the overall weight and maneuverability of the scooter.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Lighter and more compact, which can make the scooter easier to handle and transport, and can contribute to better overall scooter performance.
Lifespan and Durability:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
Generally have a shorter lifespan, often around 1-2 years with regular use. They can also be less resilient to deep discharges.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Typically last longer, often 5-7 years or more, and have a higher number of charge cycles. They are also more resistant to deep discharges and have a lower rate of performance degradation over time.
Performance in Extreme Conditions:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
Performance can be affected by extreme temperatures, with reduced efficiency in cold conditions.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Generally perform better in a wider range of temperatures and are more resistant to temperature-related performance issues.
Environmental Impact:
Lead-Acid Batteries:
Have a larger environmental impact due to the disposal of hazardous materials and the need for recycling.
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Although they also require recycling, they are less harmful to the environment compared to lead-acid batteries and have a smaller overall environmental footprint due to their longer lifespan and higher efficiency.
While lead-acid batteries are more traditional and cost-effective, lithium-ion batteries offer significant advantages in terms of weight, lifespan, charging time, and performance. The choice of battery technology can affect the overall user experience, including range, maintenance needs, and the convenience of using a 4-wheel mobility scooter.


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch







-3.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)
.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)