How does the design of the steering mechanism in a 3 wheels elderly mobility scooter influence maneuverability and handling?
The design of the steering mechanism in a 3-wheeled elderly mobility scooter plays a crucial role in influencing its maneuverability and handling. Here’s how different design aspects impact these factors:
1. Steering Type
Handlebar Steering: Many 3-wheeled scooters use handlebars for steering, which allows for direct and intuitive control. This type of steering is often favored for its ease of use and precision, particularly in tight spaces.
Delta or T-Bar Steering: Some models use a delta or T-bar steering mechanism, where the steering is controlled by a bar in front of the user. This design can enhance stability and control, making it easier to navigate through narrow spaces and make tight turns.
2. Front Wheel Configuration
Single Front Wheel: In a 3-wheeled scooter with a single front wheel, the steering mechanism typically involves pivoting the front wheel to change direction. This configuration can provide a tighter turning radius but may affect stability at higher speeds or on uneven surfaces.
Dual Front Wheels: Some 3-wheeled scooters feature two front wheels, which can provide improved stability and more balanced steering. This setup can help distribute weight more evenly and enhance maneuverability, especially on rough or uneven terrain.
3. Turning Radius
Smaller Turning Radius: The design of the steering mechanism affects how sharply the scooter can turn. A well-designed steering system allows for a smaller turning radius, making it easier to navigate tight corners and confined spaces.
Variable Steering Angles: Some scooters have adjustable steering angles, which can be modified based on the user’s needs or the environment, further enhancing maneuverability.
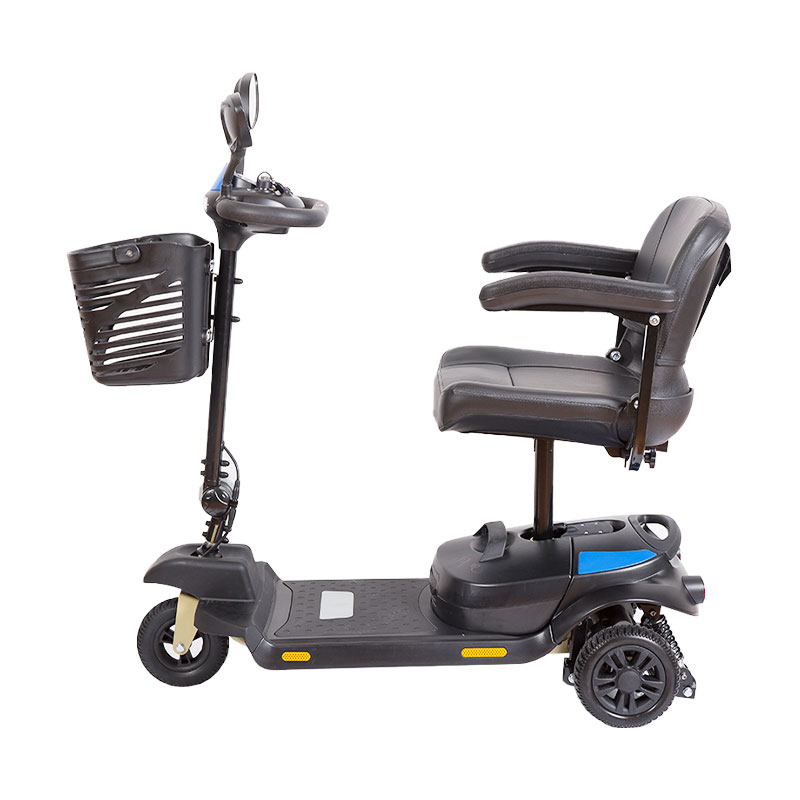

4. Control Sensitivity
Precise Control: The sensitivity of the steering controls affects how easily the scooter responds to user inputs. A design that allows for fine control enables smoother and more accurate maneuvering, which is particularly important for elderly users who may have limited strength or dexterity.
Responsiveness: The responsiveness of the steering mechanism impacts how quickly the scooter reacts to changes in direction. A well-designed system ensures that the scooter handles smoothly and predictably, improving overall handling.
5. Ergonomics
Comfort and Reach: The steering mechanism should be ergonomically designed to ensure that it is comfortable and easy to reach for users of different sizes and physical abilities. Properly positioned controls reduce strain and improve ease of operation.
Adjustability: Adjustable steering mechanisms allow users to customize the steering setup to their preferences, which can enhance both comfort and control.
6. Stability and Safety
Impact on Stability: The steering design affects the scooter’s stability. For instance, a well-designed front suspension system combined with effective steering can help absorb shocks and maintain balance, contributing to safer handling.
Safety Features: Some scooters incorporate safety features like speed limiters or automatic steering corrections to prevent tipping or loss of control, which enhances overall maneuverability and handling.
The design of the steering mechanism in a 3-wheeled mobility scooter is pivotal in determining its maneuverability and handling. Features such as steering type, front wheel configuration, turning radius, control sensitivity, ergonomics, and stability all contribute to how easily and effectively the scooter can be navigated. A well-designed steering system enhances the scooter’s responsiveness, stability, and overall ease of use, making it more suitable for elderly users and various environments.


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch







-3.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)
.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)