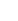
How does the design of a four-wheel mobility scooter contribute to enhanced stability and balance?
The design of a four-wheel mobility scooter is deliberately crafted to provide more desirable balance and balance, essential factors for making sure a safe and assured driving revel in. Several design elements make a contribution to these attributes:
Wheel Configuration:
The four-wheel configuration inherently offers a stable foundation. Placing wheels at the front and two at the rear creates a balanced wheelbase, dispensing the scooter's weight calmly. This format minimizes the threat of tipping and complements basic balance.
Centralized Seating Position:
The positioning of the person's seating place among the front and rear wheels is a key design attention. This centralized placement optimizes stability by using aligning the person's weight with the geometric center of the scooter. It facilitates save you instability throughout turns, stops, or changes in terrain.
.jpg)
Low Center of Gravity:
The layout regularly incorporates a low middle of gravity, in which the bulk of the scooter's mass is situated closer to the ground. This design characteristic complements stability with the aid of lowering the ability for tipping, particularly whilst navigating slopes or choppy surfaces.
Suspension System:
Effective suspension structures are included to absorb shocks and vibrations from uneven terrain. By providing a smoother trip, the suspension contributes to retaining balance, ensuring that the scooter stays balanced even on hard surfaces.
Robust Frame Construction:
The body of a four-wheel mobility scooter is designed to be sturdy and rigid. This creation minimizes flexing or wobbling, contributing to normal balance. A strong frame is essential for retaining stability throughout various actions and transitions.
Wide and Solid Base:
The width of the scooter's base is cautiously considered to provide a solid and large footprint. A wider base complements stability by means of dispensing the weight over a bigger region, lowering the chance of tipping, particularly at some point of turns.
Balanced Weight Distribution:
The design prioritizes balanced weight distribution across the scooter. This guarantees that the load is frivolously unfold between the front and rear wheels, stopping imbalances that would compromise balance.
Intuitive Steering Mechanism:
The steerage mechanism is designed to be intuitive and responsive. Smooth and controlled steering enhances the user's potential to keep stability, particularly when navigating thru tight areas or making unique maneuvers.
Tire Grip and Traction:
The tires are designed to provide top of the line grip and traction on diverse surfaces. This guarantees that the scooter maintains stability even on slippery or choppy terrain, improving user confidence for the duration of outside sports.
In summary, the complete layout of a 4-wheel mobility scooter considers elements together with wheel configuration, seating function, middle of gravity, suspension, body production, base width, weight distribution, steerage, and tire traction. These factors work collectively harmoniously to create a mobility solution that prioritizes more advantageous balance and balance, in the end supplying customers with a dependable and steady mode of transportation.


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch







-3.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)
.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)